Objective: Evaluate an application, its usability, user experience, interface, and overall effectiveness in providing immersion and engagement
Engage VR is a versatile platform catering to enterprise and educational professionals. It offers various services in spatial computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the metaverse. Engage VR provides a comprehensive solution across various devices, including PCs, and mobile, designed to support training, events, development, onboarding, and educational use cases.
As a practitioner within Higher Education, I have had the opportunity to explore immersive tech authoring tools and experiment with technologies to enhance the student experience. I have delved into Engage VR as an end-user exploring experiences and as a facilitator leveraging its capabilities for educational purposes.
Beyond educational content, one notable experience within Engage VR is the Fat Boy Slim concert in the metaverse, which left a lasting impression. The immersive journey through various scenes, including zorbing, motorcycle rides, and dancing on trucks, captured the essence of a virtual festival, eliciting excitement and engagement. It was a prime example of how XR experiences transport users to unique and captivating environments.
Video recorded by Kerry Steele-Jones
Additionally, as part of our exploration into immersive tech, we have delved into ready-made content downloadable to Meta Quest 2, such as during an introduction to VR workshop for nursing students. By testing and examining various VR medical apps, students were able to provide valuable feedback on their likes, dislikes, and the potential utility of VR in their field.
While exploring other applications, the functionality fell short of Engage VR. The ability to create persistent spaces and customise them to suit our needs has been a game-changer. For instance, working with students to create content for a Wellbeing Conference showcased the platform’s versatility and potential for fostering immersive learning experiences. Furthermore, integrating Engage VR into faculty training days proved invaluable in introducing VR technology and the platform’s capabilities to educators. It demonstrated how immersive technologies can enhance teaching and learning, fostering creativity, engagement, and collaboration.
Moreover, Engage VR has enhanced our applicant open days, particularly for potential fashion and marketing experiences. The platform provided an immersive and interactive showcase, leaving a lasting impact on attendees and generating significant interest in the programs.
In essence, Engage VR stands out as a comprehensive platform that offers immersive experiences and empowers educators and professionals to harness the potential of XR technologies for impactful learning, engagement, and marketing experiences.
Affordances within Engage VR:
Engage VR effectively integrates affordances into its interface and interactions, guiding users intuitively through virtual environments. For example:
Affordance: Interacting with virtual elements based on physical movement in the real world - Teleportation Feature [Spatial Interaction]
The teleporting feature in Engage VR allows users to jump to a new position within the virtual environment quickly. Users can navigate and move within the virtual space by selecting a destination point indicated by a landing circle. If the landing circle turns red, the chosen location is inaccessible for teleportation. This feature is designed to enhance navigation and movement within Engage’s virtual spaces.
Engage VR offers various other spatial interactions beyond gestures and tools to enhance user engagement and immersion. For instance, users can interact with virtual objects by reaching out to grab them and manipulating elements by moving their bodies within the VR space.
Spatial Interaction: In VR, users can navigate and interact with digital content in a spatial manner. This introduces new ways of designing UI elements and controls. Instead of relying solely on buttons and menus, designers can explore intuitive gestures, hand-tracking, and spatial interfaces to enhance usability and create natural interactions.
(Resource, 2023)
(Engage, 2022)
Affordance: Pressing or Selecting Buttons to Trigger Actions
Engage VR implements clickable buttons within the VR environment to facilitate interaction with menus, options, and UI elements. Instead of relying solely on traditional buttons or menus, the platform introduces innovative interfaces that mimic real-life interactions, enhancing user engagement and immersion.
- Virtual Watch: Users can flick their arm around, simulating the action of checking a real-life watch. The interface resembles a watch, with buttons and controls that users can press to perform various actions. This design choice aligns with the principle of affordance, as users naturally understand that pressing buttons on a watch-like interface triggers actions, mirroring real-world interactions.
- iPad-like Device: Engage VR incorporates an iPad-like device within the virtual environment, allowing users to take pictures and access various controls and functionalities. Users interact with the iPad by pressing buttons and controls using their controllers, mimicking the experience of using an iPad. This approach enhances user understanding and engagement by leveraging familiar interaction patterns and affordances from real-life devices.

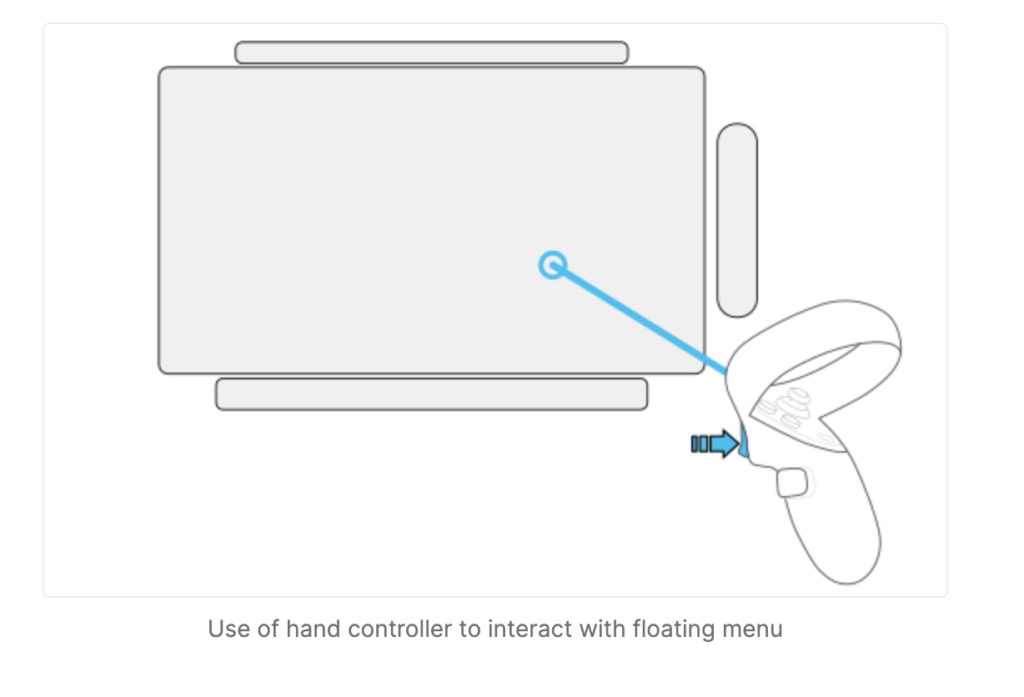
Affordance: Interacting with Virtual Objects through Manipulation
Engage VR enables users to interact with virtual objects seamlessly by leveraging handheld controllers or hand-tracking technology within the VR environment. This affordance empowers users to pick up, move, rotate, and manipulate virtual objects precisely and easily, enhancing immersion and interaction within the virtual space.
- Picking Up Objects: Users can reach out and grab virtual objects within the environment using their controllers or hand gestures, mirroring the action of picking up objects in real life.
- Moving and Rotating Objects: Once an object is picked up, users can freely move and rotate it within the virtual space, allowing for precise positioning and arrangement. This functionality enables users to interact with virtual objects in a dynamic and responsive manner.
- Manipulating Object Properties: Engage VR goes beyond basic interaction by allowing users to manipulate object properties such as size. Users can adjust these properties using intuitive gestures or controller inputs, fostering creativity and customisation within the virtual environment.
Grounding within Engage VR:
Grounding can be experienced in various ways to enhance the sense of immersion and presence in virtual environments. For example:


Engage VR provides customers with immersive pre-made virtual environments, which is useful for planning workshops and creating experiences. The platform brings virtual spaces to life and helps to bridge the gap between the real world and the virtual world.
Premade Environments for Wellbeing Conference:
Working with MA students, we created an experience where users could explore the 5 steps to wellbeing. In the classroom setting, we implemented a language taster course to teach Tamil, which was helpful for the “learn” step.
Classroom Environment:
Features such as desks, chairs, and whiteboards contribute to grounding by creating a familiar setting for users. The spatial layout and acoustics simulate those of a traditional classroom, enhancing the sense of immersion and presence.
Forest Space Features for Grounding:
One of the steps was aimed towards wellbeing and to take notice of your surroundings. Our experience allowed users to explore a virtual forest and immerse themselves in the sounds of nature, including bird songs and water.
The forest space includes realistic features such as trees, foliage, and natural sounds (like birds chirping or rustling leaves). These features contribute to grounding by replicating the sights and sounds of a real forest. Users can feel truly immersed in nature, promoting relaxation and mindfulness during the wellbeing conference.
My Fat Boy Slim Experience:
Club Entrance Simulation: Waiting outside the club for the Fat Boy Slim concert to begin created anticipation and realism, mimicking the real-world experience of waiting in line to enter a venue and enhancing grounding by immersing users in a familiar scenario, setting the stage for the main event and strengthening the overall sense of presence and immersion.
You can ground the user with virtual cockpits, chairs, or other stationary objects to explain why they are sitting — despite the fact that VR shows them moving. If the user is near a very large virtual object that is moving, they may mistakenly believe that they are moving, as opposed to the large object moving. This may cause discomfort. Avoid this by including more fixed points of reference in the user’s environment.
(Korovkina 🇺🇦, 2020)
Immersion within Engage VR:
immersion is intended to instil a sense of belief that one has left the real world and is now "present" in the virtual environment.
(Mestre, 2005)
Fat Boy Slim Experience
As we waited outside the virtual venue for the Fat Boy Slim VR Experience, it felt like we were actually queuing outside a real club, eagerly anticipating a night of festivities. Before entering, we had the option to customise our avatars with Fat Boy Slim merchandise, such as T-shirts, which added a personal touch to the experience. The lively chatter of other users and the far-off sound of music from inside the virtual venue heightened the excitement and anticipation. Moreover, the ability to take selfies on our tablets added a playful element to the pre-concert atmosphere.
The immersive qualities of the Fat Boy Slim VR Concert were simply remarkable. From the pulsating music to the vibrant colours and dynamic lighting, every aspect of the experience contributed to the sensation of being present at a real festival. As I navigated through the virtual space, interacting with objects like zorbing spheres and motorcycles, I was fully engrossed in the moment, despite the awareness that these actions were virtual. The seamless transition between scenes, from skydiving to forest landscapes to dancing on trucks, further heightened the immersion. Even though I was aware of the virtual nature of the experience, I found myself completely immersed in the captivating world of the VR concert.
Presence, Place & Plausibility
The term "presence" in virtual reality (VR) commonly refers to the sensation of feeling present in a virtual environment. Slater et al. (2022) have identified two main components of presence, namely Place Illusion (PI) and Plausibility Illusion (Psi). PI refers to the feeling of actually being in the virtual space, while Psi pertains to the extent to which events within the virtual environment feel real or plausible, despite the knowledge that they are not.
Presence:
During the Fat Boy Slim VR Concert, I felt a strong sense of presence, as if I was truly immersed in the virtual environment. The realistic audiovisual effects, interactive elements, and dynamic scenes transported me to a world where I felt fully engaged and present. Despite knowing that I was experiencing a virtual concert, the level of immersion was so profound that it felt almost as if I were physically present at an actual festival. I did get goosebumps!
Place:
The virtual environment created for the Fat Boy Slim concert provided a vivid sense of place, capturing the essence of an immersive festival atmosphere. From the bustling crowd to the music stages and vibrant landscapes, every detail contributed to the sensation of being in a specific location. Whether I was dancing in a forest, skydiving through the clouds, or mingling with other avatars, each scene felt distinct and immersive, further enhancing the sense of place within the VR environment.
Plausibility:
The plausibility of the Fat Boy Slim VR Concert was evident in its ability to create believable and engaging experiences within the virtual world. While the events and interactions were virtual, they were presented convincingly and coherently. The seamless transitions between scenes, the realistic physics of interactive objects, and the dynamic lighting and sound effects all contributed to the overall plausibility of the experience. Despite the fantastical nature of some elements, such as riding motorcycles (which did make me dizzy) or dancing on trucks, they felt believable within the context of the virtual environment, enhancing the overall sense of immersion and presence.
Report on User Feedback and Evaluation of Engage VR Platform
The methodology used aimed to collect and analyse feedback from users who have engaged with the VR platform [Fat Boy Slim Experience and the Platform itself].
Methodology:
Feedback collection involved performing a site search on Google using the query ‘site:www.site.co.uk Engage VR Eat Sleep VR Repeat’ [from Reddit and Linked In]. Comments about the platform and reviews were also sourced from the Meta Quest App Store and Google Play. Unfortunately, Tweet Deck, which would have been utilised to search hashtags, is no longer a free service due to changes to the platform.
Data Collection and Organisation:
Comments and reviews were copied into a spreadsheet for systematic analysis. Each piece of feedback was then summarised and categorised based on its tone, content, strengths, weaknesses, and rose, bud, and thorn aspects (LUMA Institute, n.d.). This approach allowed for a comprehensive understanding of user sentiments and experiences. Strengths of the Engage VR Platform, such as its intuitive user interface and diverse range of pre-made environments, were highlighted alongside its weaknesses, including platform stability issues and limited access to advanced features. Similarly, user feedback on the Fat Boy Slim VR Experience showcased its immersive audiovisual effects as a strength while identifying limited customisation options and occasional technical glitches as weaknesses. Additionally, rose and bud aspects, reflecting positive experiences and potential areas for improvement, were identified across both the Engage VR Platform and the Fat Boy Slim VR Experience. Thorn aspects, representing challenges or negative experiences, were also noted to provide insights into areas requiring attention or enhancement. This analysis provided insights into user perspectives, guiding future improvements and developments.
Key Themes and Sentiments:
The analysis revealed several recurring themes and sentiments among users. Positive feedback centred around the platform’s intuitive user interface, a diverse range of environments, and flexible content creation tools. However, users also expressed concerns regarding platform stability, navigation challenges, and limited customisation options.
Click to view the Miro board
User Feedback Analysis:
Actionable Insights for Improvement
This section explores actionable insights for improving the user experience of the Fat Boy Slim virtual concert experience. While conducting the analysis, it’s important to note that users have reported specific technical issues, such as loading times between scenes in the Fat Boy Slim experience. However, this report will focus on actionable insights relevant to human-centered design principles. Factors influencing performance, such as internet connection and hardware specifications, are acknowledged but not directly addressed in these recommendations. By leveraging insights from user feedback, I aim to provide valuable recommendations that align with the goal of enhancing user satisfaction, engagement, and accessibility.
Fat Boy Slim Experience
Users have expressed a desire for more customisation options within the Fat Boy Slim VR experience. Giving users greater control over their avatars, environments, and personal settings can enhance immersion and personalisation. By allowing users to tailor their virtual experience to their preferences, Engage VR can cater to diverse user preferences and tastes.
Engage VR already offers basic interaction features such as pointing fingers, clapping, raised hand gestures, and emojis above avatars’ heads, as seen in the screenshots on the Miro board.
Virtual high-fives and fist bumps could be introduced to enhance user interaction and engagement. These interactive gestures allow users to express camaraderie and celebrate shared experiences during the experience. Implemented as intuitive actions that users can perform with their virtual hands, these gestures would promote a sense of unity and connection among participants. Integrating haptic feedback into the controls could enhance the immersive experience, providing tactile sensations to complement visual interactions.
Introducing photo-sharing functionality within the Engage VR platform could enhance social interactions and facilitate meaningful user connections during shared experiences. Enabling users to exchange photos with each other in real-time can promote spontaneity, creativity, and personal expression, enriching the overall immersive experience. Currently, Engage already offers the ability to take pictures but not to share them with other users. Integrating photo-sharing directly within the Engage VR platform would fill this gap and provide users a seamless way to interact and connect through visual media.
Additionally, while the Quest’s built-in recording and sharing feature offers convenience, integrating photo-sharing directly within the Engage VR platform enhances immersion and encourages spontaneous user interactions. This streamlined approach fosters a sense of cohesion and engagement within the platform’s community, promoting a vibrant and inclusive atmosphere.
Implementing robust privacy controls and moderation mechanisms is essential to protect users’ privacy and ensure a safe and positive environment for photo-sharing. By providing users with options to control who can view and interact with their photos and mechanisms to report inappropriate content or behaviour, Engage VR can maintain a secure and enjoyable experience for all users.
To expand on personalisation and customisation within the Fat Boy Slim VR experience, Engage VR could introduce various festival-themed dressing-up outfits and interactive props. Users could choose from multiple outfits, such as funky hats, colourful bandanas, and stylish sunglasses, allowing them to express their unique personalities and styles within the virtual environment. Additionally, interactive props like virtual glow sticks and illuminated headbands could be implemented, enabling users to immerse themselves fully in the festival atmosphere. These props could be passed around and shared among attendees during music performances, creating a collective celebration reminiscent of traditional festivals.





